Controlling the Water Absorbency of Agricultural Polymers

Controlling the Water Absorbency of Agricultural Polymers
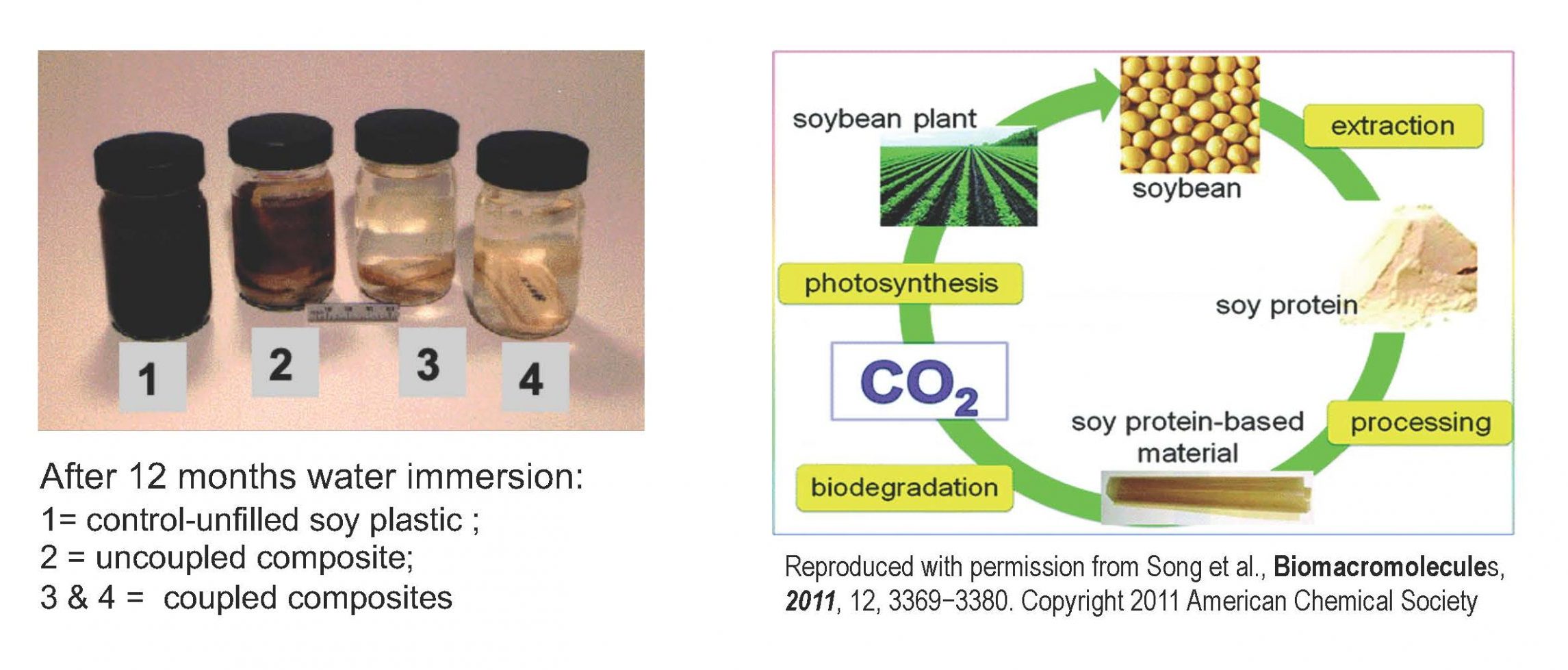
Blending special bioabsorbable polyphosphate fillers, biodegradable soy protein isolate, plasticizer, and adhesion promoter in a high-shear mixer followed by compression molding resulted in a relatively water-resistant, biodegradable soy-protein polymer composite.
Natural biodegradable polymers made from agricultural products, such as soy protein isolate and corn starch, have poorer water resistance than synthetic polymers derived from petrochemicals and thus absorb more moisture. As a result, commercial exploitation of agriculturally derived materials has been very limited. The targeted applications for the natural biodegradable polymers require that the materials have sufficient stiffness and strength during their useful life but eventually biodegrade. Achieving this required combination of properties from the biodegradable polymers is very difficult because of their inherent water sensitivity and relatively low stiffness and strength, especially in moist environments. To address these problems, the author recently initiated a long-range research project to develop affordable, stiff, strong bioabsorbable polyphosphate filler/soy protein polymer composites, along with methods for making practical shapes from these products· The research involves blending special bioabsorbable polyphosphate reinforcing fillers having low glass transition temperatures and the biodegradable soy-protein polymer using a single-screw (or twin-screw) extruder at temperatures above the polymer’s melting point. The blended soy-protein polymer composite containing the required amount of the reinforcing fillers is then either injection molded or compression molded into articles of various shapes and sizes.